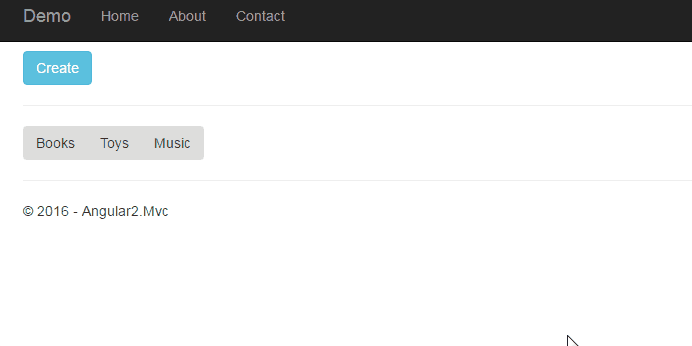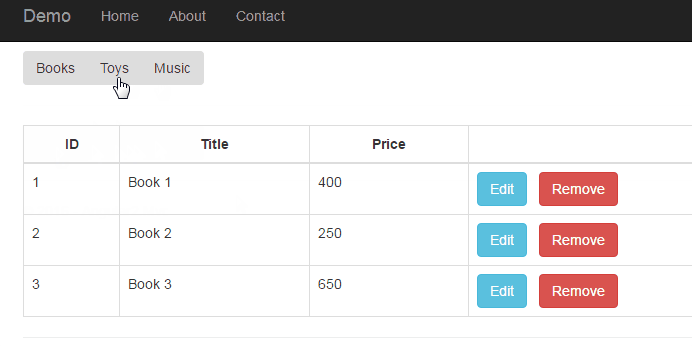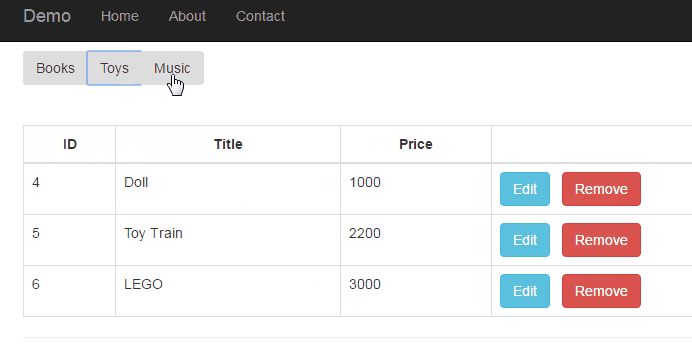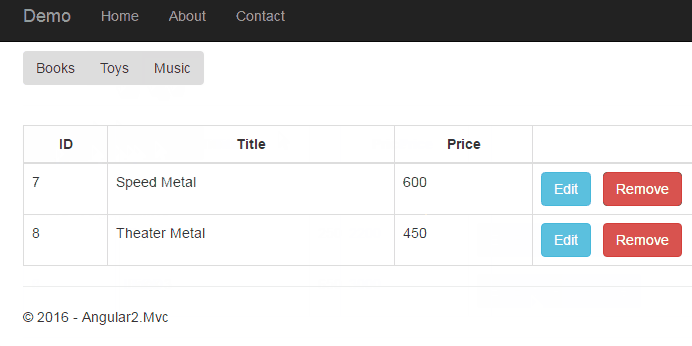
In this article, we will use sub-routing to implement the component injection to the current routing (page). The routing rules are showed as following structure.
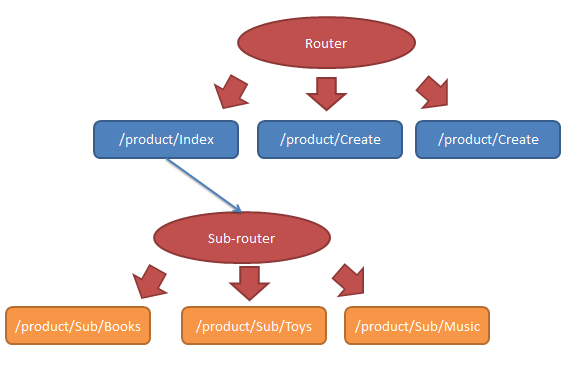
Follow the steps in Day 6 – Routing
for creating the following MVC controller/view, index component and routes config.
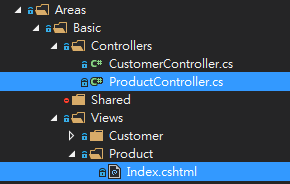
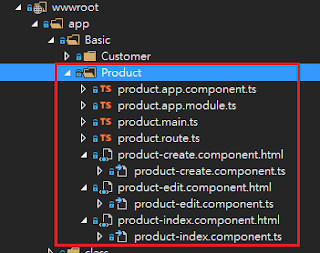
Now we have the parent routing, we will create sub-rounting at next step.
Since we will have 3 sub-routs, that means we should have the 3 components:
product-books.component
product-toys.component
product-music.component
Also we will create a product.service to provide the data.
export class Product {
Id: string;
TypeId: string;
Type: string; //Book,Toy,Music
Title: string;
Price: number;
}
import {Injectable,Inject} from '@angular/core';
import {Product} from '../../class/Product';
@Injectable()
export class ProductService {
constructor() {
}
//Get books
public getBooks() {
return new Promise<Product[]>(
resolve => {
let books = PRODUCTS.filter(x => x.Type == "Book");
resolve(books);
});
}
//Get toys
public getToys() {
return new Promise<Product[]>(
resolve => {
let toys = PRODUCTS.filter(x => x.Type == "Toy");
resolve(toys);
});
}
//Get toys
public getMusic() {
return new Promise<Product[]>(
resolve => {
let musices = PRODUCTS.filter(x => x.Type == "Music");
resolve(musices);
});
}
}
const PRODUCTS: Product[] =
[{ "Id": "1", "TypeId":"1", "Type": "Book", "Title": "Book 1", "Price": 400 },
{ "Id": "2", "TypeId":"1", "Type": "Book", "Title": "Book 2", "Price": 250 },
{ "Id": "3", "TypeId":"1", "Type": "Book", "Title": "Book 3", "Price": 650 },
{ "Id": "4", "TypeId":"2", "Type": "Toy", "Title": "Doll", "Price": 1000 },
{ "Id": "5", "TypeId":"2", "Type": "Toy", "Title": "Toy Train", "Price": 2200 },
{ "Id": "6", "TypeId":"2", "Type": "Toy", "Title": "LEGO", "Price": 3000 },
{ "Id": "7", "TypeId":"3", "Type": "Music", "Title": "Speed Metal", "Price": 600 },
{ "Id": "8", "TypeId":"3", "Type": "Music", "Title": "Theater Metal", "Price": 450 }];
import {Component, OnInit} from '@angular/core';
import {Router} from '@angular/router';
import {Product} from '../../class/Product';
import {ProductService} from './product.service';
@Component({
selector: 'product-books',
providers: [ProductService],
templateUrl: '/app/Basic/Product/product-books.component.html'
})
export class ProductBooksComponent implements OnInit {
private title: string;
private books: Product[];
constructor(
private router: Router,
private productService: ProductService
) {
this.title = "Books";
this.productService = productService;
}
ngOnInit() {
this.initBooks();
}
//Initialize books
private initBooks() {
this.productService.getBooks().then(data => {
this.books = data;
})
}
}
PS. You can implement toy and music components with almost the same codes of book component.
We need another router-outlet to inject the routes (components above).
So we create a product-sub.component for the responsibility, and put product-sub.component on product-index.component.
import {Component} from '@angular/core';
import {Router} from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'product-sub',
providers: [],
template: '<div class="btn-group" role= "group" aria-label="Basic example">'+
'<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" (click)="goToBooks()">Books</button>'+
'<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" (click)="goToToys()">Toys</button>' +
'<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" (click)="goToMusic()">Music</button>'+
'</div>' +
'<router-outlet></router-outlet>'
})
export class ProductSubComponent {
constructor(private router: Router) {
}
private goToBooks() {
//Go to book route
}
private goToToys() {
//Go to toy route
}
private goToMusic() {
//Go to music route
}
}
The product-sub.component currently cannot navigate to the any sub-routes, we will fix this by create the sub-routes configuration later.
Now put the product-sub.component on index component.
<product-sub></product-sub>
Finally, we come to the most important part. We will add the sub-routes:
Basic/Product/Sub
| — Basic/Product/Sub/Books
| — Basic/Product/Sub/Toys
| — Basic/Product/Sub/Music
to the exist route rules.
The following routes could be set like this…
{
path: 'Basic/Product/Sub',
component: ProductSubComponent,
children: [
{ path: 'Books', component: ProductBooksComponent },
{ path: 'Toys', component: ProductToysComponent },
{ path: 'Music', component: ProductMusicComponent }
]
}
Let's take a look at the completed routes config.
import { ModuleWithProviders } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { ProductIndexComponent} from './product-index.component';
import { ProductCreateComponent} from './product-create.component';
import { ProductEditComponent} from './product-edit.component';
import { ProductSubComponent} from './product-sub.component';
import { ProductBooksComponent} from './product-books.component';
import { ProductToysComponent} from './product-toys.component';
import { ProductMusicComponent} from './product-music.component';
const appRoutes: Routes = [
{ path: 'Basic/Product/Index', component: ProductIndexComponent },
{ path: 'Basic/Product/Create', component: ProductCreateComponent },
{ path: 'Basic/Product/Edit/:id', component: ProductEditComponent },
{
path: 'Basic/Product/Sub',
component: ProductSubComponent,
children: [
{ path: 'Books', component: ProductBooksComponent },
{ path: 'Toys', component: ProductToysComponent },
{ path: 'Music', component: ProductMusicComponent }
]
},
{ path: '', redirectTo: '/Basic/Product/Index', pathMatch: 'full' }
];
export const ProductRoutes: ModuleWithProviders = RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes);
And don't forget to update product-sub.component.
//...
export class ProductSubComponent {
constructor(private router: Router) {
}
private goToBooks() {
this.router.navigate(['Basic/Product/Sub', 'Books']);
}
private goToToys() {
this.router.navigate(['Basic/Product/Sub', 'Toys']);
}
private goToMusic() {
this.router.navigate(['Basic/Product/Sub', 'Music']);
}
}